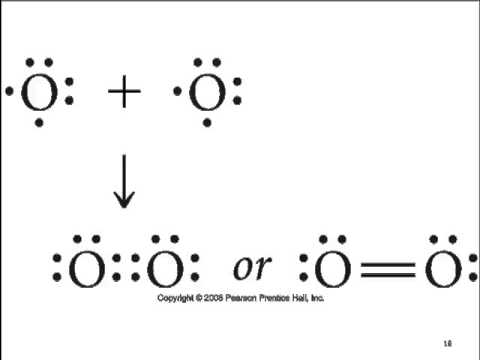

Given descriptions, diagrams, scenarios, or chemical symbols, students will model covalent bonds using electron dot formula (Lewis structures). Dec 30, 2013 There are three basic steps to determining the bond angles in a molecule: 1. Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Assume that you must determine the bond angles in 'BF'3. 'B' is less electronegative than 'F', so 'B' becomes the central atom. If we have three 'F' atoms, that means that we are going to use all three electrons from the 'B'. This gives us three bonding pairs of.
In 1916, ten years before the Schrodinger wave equation, G. N. Lewis suggested that a chemical bond involved sharing of electrons. He described what he called the cubical atom
, because a cube has 8 corners, to represent the outer valence shell electrons which can be shared to create a bond. This was his octet rule.
- Count the number of valence e- each atom brings into the molecule.For ions, the charge must be taken into account.
How many valence electrons in BeCl2?
How many valence electrons in NO2- and NO2+?
- Put electron pairs about each atom such that there are 8 electrons around each atom (octet rule), with the exception of H, which is only surrounded by 2 electrons. Sometimes it's necessary to form double and triple bonds. Only C, N, O, P and S (rarely Cl) will form multiple bonds.
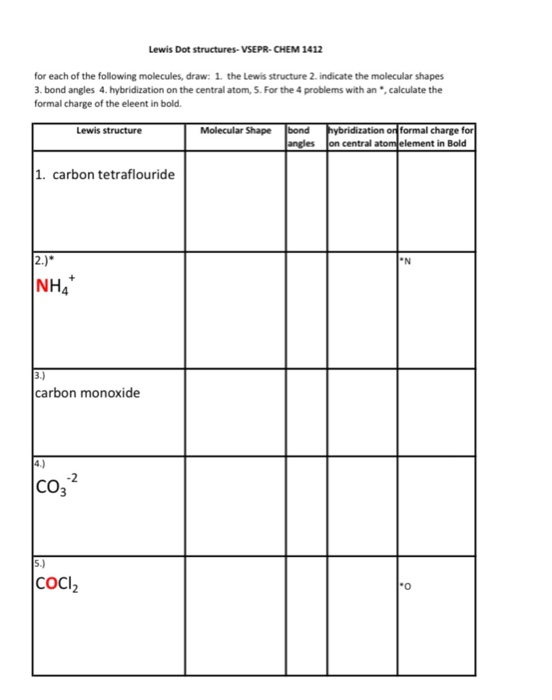
Draw the Lewis dot structure for CF4.
The number of valence electrons is 4 + 4 ( 7 ) = 32 electrons.
So, we obtain:
Draw the Lewis dot structure for CO.
The number of valence electrons is 4 + 6 = 10 electrons or 5 pairs. Since both C and O allow multiple bonds we can still follow the octet and write:
- If there is not enough electrons to follow the octet rule, then the least electronegative atom is left short of electrons.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for BeF2.
In BeF2 number of valence e- = 2+ 2(7) = 16 e- or 8 pairs. Since neither Be or F form multiple bonds readily and Be is least electronegative we obtain:
- If there are too many electrons to follow the octet rule, then the extra electrons are placed on the central atom.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for SF4.
In SF4 the number of valence electrons is 6 + 4 ( 7 ) = 34 electrons or 17 pairs. Placing the extra electrons on S we obtain:
How can the octet rule be violated in this last example? The octet rule arises because the s and p orbitals can take on up to 8 electrons. However, once we reach the third row of elements in the periodic table we also have d-orbitals, and these orbitals help take the extra electrons. Note that you still need to know how the atoms are connected in a polyatomic molecule before using the Lewis-Dot structure rules.

Homework from Chemisty, The Central Science, 10th Ed.
8.45, 8.47, 8.49, 8.51, 8.53, 8.55, 8.57, 8.59, 8.61, 8.63
Lewis Structure Finder
|